CK迁移
Clickhouse数据迁移,将一个表的数据,拷贝到另一个表或远程服务器上,有四种常用的方式:
- 方法一:先将数据导出为
TSV或CSV文件,再利用clickhouse-client --query命令导入 - 方法二:利用
insert into ... select语句,加上remote可以选择从远程数据库导入
insert into ... select * from remote('ip',db.table,'user','password')
- 方法三:clickhouse-copier工具
这个工具网上推荐比较多,是官方的数据迁移工具,主要用在多个集群之间的数据迁移 - 方法四:直接拷贝原始数据文件,再
ATTACH即可
笔者喜欢使用第四种方式,简单粗暴,直接从磁盘拷贝,速度很快。下面演示具体步骤。
数据文件拷贝方式
假设使用默认数据库
default,我们要拷贝的表名为test。
步骤一
进入clickhouse数据目录,拷贝对应的数据文件
> cd /var/lib/clickhouse/data/default
> ls
test
复制test文件夹(test即表名)到目标机器相同路径下。
步骤二
进入metadata目录
> cd /var/lib/clickhouse/metadata/default
> ls
test.sql
这里有个test.sql,这个其实就是我们建表语句,只不过把CREATE替换了ATTACH而已。
复制里面SQL语句,并在目标机器执行,然后show tables,可以发现数据已成功导入。
背景
大约在 2018 年 8 月份开始正式接触 ClickHouse,当时机房没有合适的服务器,就在 Azure 开了一台虚拟机来部署。平稳运行了两年,支撑了 YiDrone 和 YiSonar 两个重要的产品的底层数据存储和查询。前段时间采购服务器的时候预留了一些资源,加上 Azure 的免费订阅即将到期,于是准备把 ClickHouse 迁回到机房。数据量不大,只有一个节点,硬盘上的数据加起来 500G 左右。
方案调研
迁移集群实际上就是要把所有数据库(system 除外)的表结构和数据完整的复制一遍。ClickHouse 官方和社区有一些现成的解决方案,也可以自己实现。
拷贝数据目录
先观察一下 ClickHouse 在文件系统上的目录结构(配置文件 /ect/clickhouse-server/config.xml 里面配置的 <path>),为了便于查看,只保留了 data 和 metadata 目录。
.├── data│ ├── default│ ├── system│ │ ├── asynchronous_metric_log│ │ ├── metric_log│ │ ├── query_log│ │ ├── query_thread_log│ │ └── trace_log├── metadata│ ├── default│ │ └── v_table_size.sql│ ├── default.sql│ ├── system│ │ ├── asynchronous_metric_log.sql│ │ ├── metric_log.sql│ │ ├── query_log.sql│ │ ├── query_thread_log.sql│ │ └── trace_log.sqldata目录里保存的是数据,每个数据库一个目录,内部每个表一个子目录。metadata目录里保存的是元数据,即数据库和表结构。其中<database>.sql是 创建数据库的 DDL(ATTACH DATABASE default ENGINE = Ordinary)<database>/<table>.sql是建表的 DDL (ATTACH TABLE ...).
这里的 DDL 使用的是
ATTACH语句, 进入文档 查看 ATTACH 的作用及跟 CREATE 的区别
基于这个信息,直接把 data 和 metadata 目录(要排除 system)复制到新集群,即可实现数据迁移。用一个小表做测试,验证可行。
操作流程
- 在源集群的硬盘上打包好对应数据库或表的 data 和 metadata 数据
- 拷贝到目标集群对应的目录
- 重启 clickhouse-server
使用 remote 表函数
ClickHouse 除了查询常规的表,还能使用表函数来构建一些特殊的「表」,其中 remote 函数 可用于查询另一个 ClickHouse 的表。
使用方式很简单:
SELECT * FROM remote('addresses_expr', db, table, 'user', 'password') LIMIT 10;因此,可以借助这个功能实现数据迁移:
INSERT INTO <local_database>.<local_table>SELECT * FROM remote('remote_clickhouse_addr', <remote_database>, <remote_table>, '<remote_user>', '<remote_password>')操作流程
- 在源集群的
system.tables表查询出数据库、表、DDL、分区、表引擎等信息 - 在目标集群上,运行 DDL 创建表,然后运行上述迁移语句复制数据
- 遍历所有表,执行 2
使用 clickhouse-copier
Clickhouse-copier 是 ClickHouse 官方提供的一款数据迁移工具,可用于把表从一个集群迁移到另一个(也可以是同一个)集群。Clickhouse-copier 使用 Zookeeper 来管理同步任务,可以同时运行多个 clickhouse-copier 实例。
使用方式:
clickhouse-copier --daemon --config zookeeper.xml --task-path /task/path --base-dir /path/to/dir其中 --config zookeeper.xml 是 Zookeeper 的连接信息,--task-path /task/path 是 Zookeeper 里任务配置的节点路径。在使用时,需要先定义一个 XML 格式的任务配置文件,上传到 /task/path/description 里。同步任务是表级别的,可以配置的内容还比较多。Clickhouse-copier 可以监听 /task/path/description 的变化,动态加载新的配置而不需要重启。
操作流程
- 创建
zookeeper.xml - 创建任务配置文件,格式见官方文档,每个表都要配置(可使用代码自动生成)
- 把配置文件内容上传到 Zookeeper
- 启动 clickhouse-copier 进程
理论上 clickhouse-copier 运行在源集群或目标集群的环境都可以,官方文档推进在源集群,这样可以节省带宽。
使用 clickhouse-backup
clickhouse-backup 是社区开源的一个 ClickHouse 备份工具,可用于实现数据迁移。其原理是先创建一个备份,然后从备份导入数据,类似 MySQL 的 mysqldump + SOURCE。这个工具可以作为常规的异地冷备方案,不过有个局限是只支持 MergeTree 系列的表。
操作流程
- 在源集群使用
clickhouse-backup create创建备份 - 把备份文件压缩拷贝到目标集群
- 在目标集群使用
clickhouse-backup restore恢复
对比
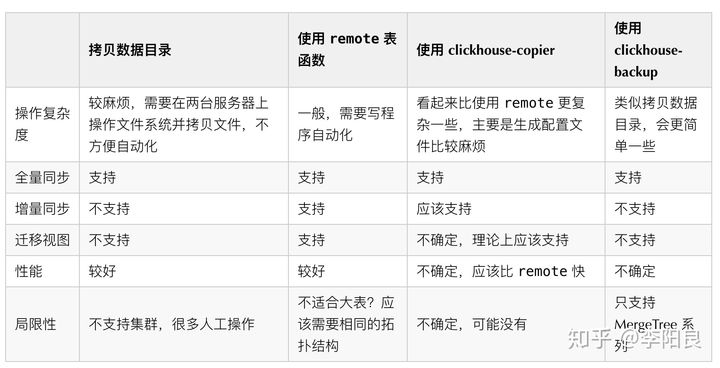
从官方和社区的一些资料综合来看 clickhouse-copier 功能最强大,不过考虑到数据量较少,而且对 clickhouse-copier 有些地方也不是很清楚,最终决定使用 remote 函数来做数据迁移。
关于别的数据迁移方案、更多的 clickhouse-copier 使用案例,可参考 Altinity 的博客 Clickhouse-copier in practice.
使用 remote 函数做数据迁移
使用 remote 函数还能实现更多特性:
- 对于分区表,可逐个分区进行同步,这样实际上同步的最小单位是分区,可以实现增量同步
- 可方便集成数据完整性(行数对比)检查,自动重新同步更新过的表
代码
代码如下,需要先安装 clickhouse-driver
import collectionsimport datetimeimport functoolsimport loggingimport time from clickhouse_driver import Client source_conn = Client(host='source-host', user='user', password='password')target_conn = Client(host='target-host', user='user', password='password') def format_partition_expr(p): if isinstance(p, int): return p return f"'{p}'" def execute_queries(conn, queries): if isinstance(queries, str): queries = queries.split(';') for q in queries: conn.execute(q.strip()) class Table(object): def __init__(self, database, name, ddl, partition_key, is_view): self.database = database self.name = name self.ddl = ddl.replace('CREATE TABLE', 'CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS') self.partition_key = partition_key self.is_view = is_view def exists(self, conn): q = f"SELECT name FROM system.tables WHERE database = '{self.database}' AND name = '{self.name}'" return len(conn.execute(q)) > 0 def get_partitions(self, conn): partitions = [] q = f'SELECT {self.partition_key}, count() FROM {self.identity} GROUP BY {self.partition_key} ORDER BY {self.partition_key}' partitions = collections.OrderedDict(conn.execute(q)) return partitions def get_total_count(self, conn): q = f'SELECT COUNT() FROM {self.identity}' return conn.execute(q)[0][0] def check_consistency(self): if not self.exists(target_conn): return False, None source_ttl_count = self.get_total_count(source_conn) target_ttl_count = self.get_total_count(target_conn) if source_ttl_count == target_ttl_count: return True, None if not self.partition_key: return False, None source_partitions = self.get_partitions(source_conn) target_partitions = self.get_partitions(target_conn) bug_partitions = [] for p, c in source_partitions.items(): if p not in target_partitions or c != target_partitions[p]: bug_partitions.append(p) return False, bug_partitions def create(self, replace=False): target_conn.execute(f'CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS {self.database}') if self.is_view: replace = True if replace: target_conn.execute(f'DROP TABLE IF EXISTS {self.identity}') target_conn.execute(self.ddl) def copy_data_from_remote(self, by_partition=True): self.create() if self.is_view: logging.info('ignore view %s', self.identity) return is_identical, bug_partitions = self.check_consistency() if is_identical: logging.info('table %s has the same number of rows, skip', self.identity) return if self.partition_key and by_partition: for p in bug_partitions: logging.info('copy partition %s=%s', self.partition_key, p) self._copy_partition_from_remote(p) else: self._copy_table_from_remote() def _copy_table_from_remote(self): queries = f''' DROP TABLE {self.identity}; {self.ddl}; INSERT INTO {self.identity} SELECT * FROM remote('{source_conn.host}', {self.identity}, '{source_conn.user}', '{source_conn.password}') ''' execute_queries(target_conn, queries) def _copy_partition_from_remote(self, partition): partition = format_partition_expr(partition) queries = f''' ALTER TABLE {self.identity} DROP PARTITION {partition}; INSERT INTO {self.identity} SELECT * FROM remote('{source_conn.host}', {self.identity}, '{source_conn.user}', '{source_conn.password}') WHERE {self.partition_key} = {partition} ''' execute_queries(target_conn, queries) @property def identity(self): return f'{self.database}.{self.name}' def __str__(self): return self.identity __repr__ = __str__ def get_all_tables() -> [Table]: # 查询出所有用户的数据库和表,包括视图。视图依赖其他表,所以放到最后。 q = ''' SELECT database, name, create_table_query, partition_key, engine = 'View' AS is_view FROM system.tables WHERE database NOT IN ('system') ORDER BY if(engine = 'View', 999, 0), database, name ''' rows = source_conn.execute(q) tables = [Table(*values) for values in rows] return tables def copy_remote_tables(tables): for idx, t in enumerate(tables): start_time = datetime.datetime.now() logging.info('>>>> start to migrate table %s, progress %s/%s', t.identity, idx+1, len(tables)) t.copy_data_from_remote() logging.info('<<<< migrated table %s in %s', t.identity, datetime.datetime.now() - start_time) def with_retry(max_attempts=5, backoff=120): def decorator(f): @functools.wraps(f) def inner(*args, **kwargs): attempts = 0 while True: attempts += 1 logging.info('start attempt #%s', attempts) try: f(*args, **kwargs) except Exception as e: if attempts >= max_attempts: raise e logging.exception('caught exception') time.sleep(backoff) else: break return inner return decorator @with_retry(max_attempts=10, backoff=60)def main(): tables = get_all_tables() logging.info('got %d tables: %s', len(tables), tables) copy_remote_tables(tables) if __name__ == '__main__': main()使用方式:直接运行即可,挂了重跑,不会有副作用。
局限性
仅通过对比行数来判断数据同步完整,没有比较内部数据的一致性,因此如果上游表行数不变,更新了部分字段,将无法自动识别,需要先从目标库里把表删掉重新同步。
